 Some artists create with paint. Some artists create with sound. Some artists create with words. Jerzy Stanislaw Alexandrowicz was an artist who created with methylene blue.
Some artists create with paint. Some artists create with sound. Some artists create with words. Jerzy Stanislaw Alexandrowicz was an artist who created with methylene blue.Methylene blue is a straightforward vital stain, and many kids school use it today to see cells under a microscope. But Alexandrowicz took the simple stain to new scientific heights. An obituary gives some idea of his mastery, describing his technique as “legendary,” and his skills so renown that scientists from all over came to visit his lab to learn his methods. (The obituary, incidentally, is well worth reading and paints a picture of a rather remarkable man.)
Alexandrowicz first noted small sensory organs in the tail of crustaceans in the 1930s, but didn’t get to finish the work until after World War II, and published the discovery until 1951. He termed these “muscle receptor organs” (MROs) because the neurons were indeed sitting along a very fine strip of muscle. I doubt the PDF does justice to the pictures in the original paper, but one can get a sense of just how detailed he was. The attentive may object to this being called a “Great moment in crayfish research,” because Alexandrowicz worked with lobsters. Although the muscle receptor organs weren’t originally described in crayfish, almost all of the work that followed was done in crayfish.
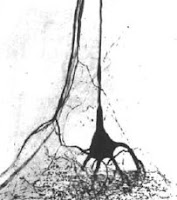 From the outset, there was interest in these little sense organs because they were readily accessible, sitting just underneath the exoskeleton and on top of the large fast flexor muscles. In contrast, similar looking organs in mammals, muscle spindle organs, were buried deep in muscles and very difficult to work with. There has been much work on them because of that, and I can only hope to hit a few highlights here.
From the outset, there was interest in these little sense organs because they were readily accessible, sitting just underneath the exoskeleton and on top of the large fast flexor muscles. In contrast, similar looking organs in mammals, muscle spindle organs, were buried deep in muscles and very difficult to work with. There has been much work on them because of that, and I can only hope to hit a few highlights here.Cornelius “Kees” Wiersma and colleagues (1953) quickly started doing physiology on these little sense organs, and explicitly drew parallels between them and vertebrate sense organs. They found that the two sensory neurons in the muscle receptor organs had very different properties. One was tonic, responding to slow and small changes, and tended to fire all the time. The other one was phasic, responding only to very hard flexions of the abdomen, and then only for one or two spikes. Wiersma and colleagues continued to do the basic legwork of tracking down the basics of the circuit (Hughes and Wiersma 1960).
Because of the neuronal connections, and the responses of isolated neurons in the dish, Larry Fields (1966) proposed that the muscle receptor organs acted in load compensation (pictured below is Figure 8 from his paper). That is, the muscle receptor organs appeared to be wired so as to detect the difference between how much bending of the tail the animal was trying to do, and how much was actually occurring. If there was a difference between those two, a reflex would kick in, activating extensor muscles to compensate for the impeded movement.

This worked with in a dish.
Unfortunately, when the muscle receptor organs were recorded from live animals performing load compensation, it seemed that the muscle receptor organs didn’t actually work that way (McCarthy and Macmillan 1999). So the function of the muscle receptor organs in intact animals, even after 50 years of work in many labs, still remains to be fully understood.
The muscle receptor organs are an “evergreen” scientific preparation, and I’ve hit on only a very, very small number of papers on them here. That I can only touch on these few highlights in a blog post is a nice example of how often, science is not about breakthroughs, but inch by inch progress.
References
Alexandrowicz JS. 1951. Muscle receptor organs in the abdomen of Homarus vulgaris and Palinurus vulgaris. Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science 92: 163-199. PDF
Fields HL. 1966. Proprioceptive control of posture in the crayfish abdomen. The Journal of Experimental Biology 44: 455-468. http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/content/abstract/44/3/455
Hughes GM, Wiersma CAG. 1960. Neuronal pathways and synaptic connexions in the abdominal cord of the crayfish. The Journal of Experimental Biology 37: 291-307. http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/content/abstract/37/2/291
McCarthy B, Macmillan D. 1999. Control of abdominal extension in the freely moving intact crayfish Cherax destructor I. Activity Of the tonic stretch receptor. The Journal of Experimental Biology 202(2): 171-181. http://jeb.biologists.org/cgi/content/abstract/202/2/171
Wiersma CAG, Furshpan E, Florey E. 1953. Physiological and pharmacological observations on muscle receptor organs of the crayfish, Cambarus clarkii Girard. The Journal of Experimental Biology 30(1): 136-151. PDF






No comments:
Post a Comment